
AI Dating Photos: Who Owns Your Data?
AI dating photo tools, like Dating Photo AI, let users upload selfies to generate polished images for dating profiles. While they promise better matches, these tools come with privacy risks. By uploading photos, you might unknowingly share biometric data, grant platforms extensive rights to your images, and allow them to use your data for AI training or marketing.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Uploaded Photos: You retain copyright, but platforms often require licenses to use your images.
- AI-Generated Photos: U.S. law doesn’t grant copyright unless there’s significant human contribution.
- Data Collection: Platforms gather metadata, facial landmarks, and usage data, which may be stored or shared.
- Data Retention: Policies vary - some delete photos quickly, others retain them for months or years.
- Control Options: You can adjust settings, request data deletion, and limit AI training use.
Before using these tools, review their terms carefully. Choose platforms with clear policies on data use, deletion, and privacy.
HACKED: The women’s dating safety app gone wrong - What in the World podcast, BBC World Service
What Data Do AI Dating Photo Tools Collect?
AI Dating Photo Data Collection: What Platforms Track and Store
When you use AI dating photo tools, the data you provide plays a dual role: it helps create personalized, high-quality images but also introduces potential privacy concerns. When uploading photos, you're essentially sharing three types of data: your original images, AI-generated outputs, and technical information. Here's a closer look at what these tools collect.
Photos You Upload
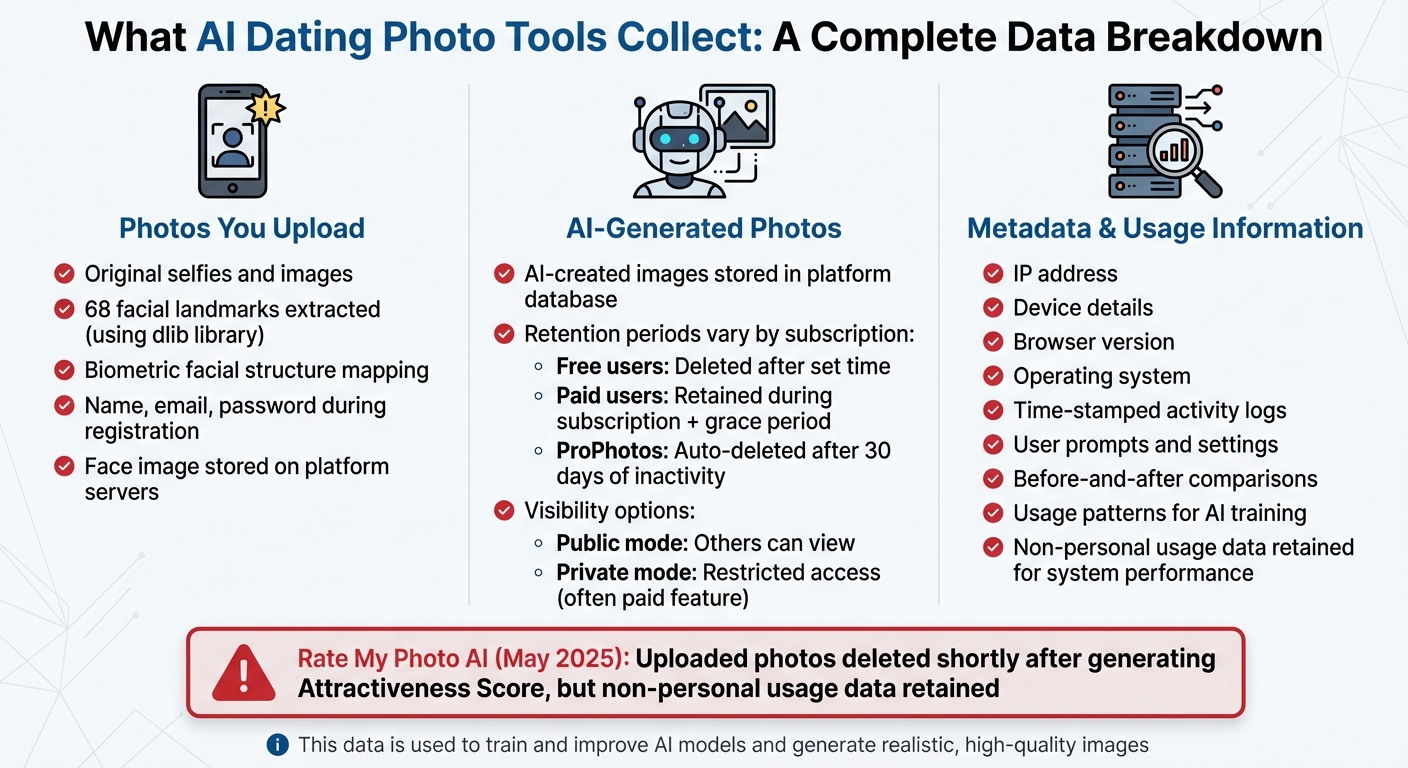
The photos you upload - such as selfies - are the starting point. Platforms like GenYOU use these images to extract 68 facial landmarks with the dlib library, creating a detailed map of your facial structure [4]. This biometric data is key to generating realistic images that closely resemble you.
"When you upload a photo, we store the face image and 68 facial landmarks extracted using the dlib library." - GenYOU Privacy Policy [4]
In addition to your photos, most platforms collect other basic details, like your name, email address, and password, during registration [3]. These practices directly affect how much control you have over who can access your personal images.
AI-Created Photos
Once the AI generates new images, they too become part of the platform's database. The retention period for these images depends on your subscription type. For instance, free users often have their images deleted after a set time, while paid users' images are retained for the duration of their subscription plus a short grace period [4]. On ProPhotos, AI-generated models are automatically deleted after 30 days of inactivity [3].
Some platforms also let you manage the visibility of your AI-generated images. For example, "Public mode" allows others to view your photos, while "Private mode", often a paid feature, restricts access to you alone [4]. These options significantly influence how much control you have over your images.
Metadata and Usage Information
AI dating tools don’t just stop at photos - they also collect technical data tied to your interactions. This includes your IP address, device details, browser version, operating system, and time-stamped activity logs [2] [4]. For example, in May 2025, Rate My Photo AI updated its privacy policy to clarify that while uploaded photos are deleted shortly after generating an "Attractiveness Score", non-personal usage data is retained to monitor system performance [7].
Additionally, platforms track how you use the tool - such as the prompts you write, settings you tweak, and any before-and-after comparisons you create. This data is often used to train and improve their AI models [4]. For instance, Dating Photo AI leverages this information to refine its ability to produce realistic, high-quality images that claim to boost users' matches on dating platforms. Understanding the scope of data collection highlights why having control over its use is so important.
Who Owns Your Original and AI-Generated Photos?
When it comes to ownership of photos - whether they’re ones you upload or those created by AI - two key areas come into play: copyright law and the platform's Terms of Service. These terms can sometimes define ownership differently than what copyright law provides.
Copyright for Your Uploaded Photos
Under U.S. copyright law, you automatically own the rights to your original photos the moment they’re created. This ownership doesn’t change even if you upload those photos to an AI-powered dating photo tool. This is especially important since it helps you maintain control over your biometric data. Major AI platforms like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Microsoft explicitly state in their Terms of Service that users retain ownership of their uploaded photos [1].
However, it’s critical to understand the distinction between ownership and licensing. While you keep the copyright to your photos, uploading them often means granting the platform a license to use them. Some platforms claim licenses that are "perpetual, worldwide, royalty-free, and irrevocable", which means they can use your photos indefinitely - even if you delete your account. For example, Snapchat’s My Selfie feature requires users to grant Snap extensive rights, including the ability to use generated images of your likeness for any purpose [5].
It’s a good idea to review the platform’s terms carefully to see if your photos may be used for marketing or AI training. Business-level tiers from providers like OpenAI and Google often come with stronger protections, such as explicit "no training by default" policies [1].
Legal Status of AI-Generated Images
While you retain copyright over your original photos, AI-generated images operate under a different legal framework. U.S. copyright law typically doesn’t grant protection to content created entirely by machines. On January 29, 2025, the U.S. Copyright Office released Part 2 of its Artificial Intelligence Report, clarifying that AI-generated outputs can only be protected if there’s meaningful human contribution. This conclusion was based on feedback from over 10,000 public comments [8].
"Extending protection to material whose expressive elements are determined by a machine... would undermine rather than further the constitutional goals of copyright." - Shira Perlmutter, Register of Copyrights and Director of the U.S. Copyright Office [8]
The report also emphasized that even if a user revises prompts multiple times, the final output reflects the AI system’s interpretation, not the user’s authorship [9]. Courts have upheld this stance, with the D.C. Circuit affirming that human authorship is a "bedrock requirement" for copyright protection, rejecting works created solely by machines [1].
To secure copyright for AI-generated photos, substantial human editing is required. For instance, using tools like Photoshop to make significant modifications can help establish human authorship. If AI serves as a tool to enhance a human-created work, the final piece may qualify for copyright protection, even if the AI-generated parts do not [8][9].
Terms of Service and Licensing Agreements
The Terms of Service you agree to when signing up for a platform play a crucial role in determining how your uploaded and generated photos can be used. These agreements often govern usage rights independently of copyright law.
Pay close attention to clauses about licensing terms, training data policies, and publicity rights. For example, some platforms include phrases like "perpetual, worldwide, royalty-free, and irrevocable", which could allow them to use your photos indefinitely. Others may specify whether your photos can be used to train AI models or appear in advertisements. Certain platforms, like Midjourney, make your prompts and images public by default unless you opt for a paid "stealth" mode [1][5].
Here’s how some platforms handle ownership and licensing:
- OpenAI and Anthropic: Allow users to own outputs as permitted by law, with no training of data for business tiers.
- Snapchat’s My Selfie: Requires granting a perpetual license and uses uploaded photos to train machine learning models.
- Midjourney: Lets users own outputs "to the fullest extent possible" but defaults to a public gallery unless you pay for stealth mode [1][5].
For greater control over your data, consider upgrading to business or enterprise tiers, which often come with stronger protections against data use and AI training [1]. Additionally, keep detailed records of your prompts and any significant edits you make. These records can help establish human authorship if you need to register or defend your work. And remember, even if you delete your account, a perpetual license may allow the platform to continue using your photos [5]. Knowing your rights is key to maintaining control over your online presence.
sbb-itb-06ba92c
How Platforms Use, Store, and Share Your Data
Understanding how AI-powered dating photo platforms handle your data is key to protecting your privacy. The process typically involves four stages: collection, processing, storage, and, in some cases, sharing. Each stage follows specific policies and practices.
Data Collection and Processing
AI dating photo platforms often start by analyzing the images you upload. For example, some use tools like dlib to map 68 facial landmarks, which helps in detecting faces and enabling realistic face-swapping [4]. Others rely on on-device processing with frameworks like Apple Vision and CoreML, which analyze your photos directly on your smartphone, ensuring they never leave your device [12].
In addition to analyzing your photos, these services collect technical metadata such as your IP address, browser type, device operating system, and referring URLs [2][10][11]. Many also use TensorFlow Lite models to predict how likely your photo is to receive likes, based on patterns from other users [12]. This combination of image analysis and metadata collection lays the groundwork for how your data is stored and managed.
Data Storage and Retention
How long your data is stored depends on the platform. Some services delete photos shortly after processing to prioritize privacy [2]. Others store images on secure cloud servers, with free users' data often retained for around three months, while paid subscribers’ data may be stored longer [4].
For other types of data, retention periods vary. For instance, many dating apps keep user data for about 90 days after an account is closed [13]. Transaction records, customer support logs, and consent forms might be retained for years - 10, 6, and 5 years, respectively [13]. Biometric data, however, is typically stored for shorter periods. Some platforms delete facial geometry data within 30 days, while others may retain facial recognition scans for up to three years [13][14].
Data Sharing and Security
Platforms exercise strict controls when sharing your data. Sometimes, user information is shared with third-party providers for tasks like hosting, analytics, payment processing, or customer support [14]. Within their own ecosystems, platforms may share data to improve matching algorithms or flag problematic accounts. For identity verification, some services collaborate with specialists who might store selfies and ID documents for up to 72 hours [14]. Additionally, platforms may share data with law enforcement when legally required.
To protect your data, platforms implement security measures such as firewalls, encrypted data transmission, and standard contractual clauses for cross-border data transfers [14]. Some AI tools that generate content from your data ensure sensitive information is deleted immediately after use. For example, Meta states:
"This information [facial features] cannot be used to identify you. This information will be used for the sole purpose of generating an edited photo and will be promptly deleted after the edited photo is generated" [6].
You can take steps to control your data by adjusting app settings to limit data collection, managing permissions through your smartphone, or disabling non-essential tracking with cookie managers. Most platforms also let you request a copy of your data or ask for its permanent deletion, although some information may still be retained for legal or safety reasons.
At Dating Photo AI, safeguarding your privacy and data security is our highest priority. We uphold rigorous data protection standards to ensure your photos and personal information remain secure at every step of the process.
Your Rights to Control Your AI Dating Photos
Taking control of your AI-generated dating photos starts with understanding how to manage your account settings and data. In a world where AI is becoming a central part of many platforms, protecting your image data is crucial for maintaining privacy and control.
Deleting Your Account and Data
Most dating platforms allow you to delete your account through in-app settings. However, simply uninstalling the app won’t erase your data. To ensure your information is removed, use the app's "Close Account" or "Delete Account" feature to start the process.
Keep in mind, deletion isn’t always instantaneous. For instance, Bumble gives users a 28-day reactivation period where your data is hidden but still stored. Alternatively, you can submit a Data Erasure Request, which may take up to 30 days. Bumble Support explains:
"If you want to erase your data right away, you can submit a Data Erasure Request to our team. This process can take up to 30 days to complete" [16].
Even after deletion, some platforms may retain specific data for legal or safety reasons. For example, Bumble stores biometric face scans for up to three years after your last activity and keeps customer support records for six years [17]. On the other hand, tools like Rate My Photo AI delete images immediately after processing [2].
Limiting Platform Use of Your Data
You can take steps to limit how platforms use your data by tweaking app settings and adjusting your smartphone permissions. This might include disabling features like facial recognition or opting out of AI training. Many apps let you disable specific features; for example, Bumble allows users to turn off its "Best Photo" algorithm, which automatically rearranges profile pictures based on popularity [19].
For tools like Google Photos that "remember" details about you, you can review and delete specific information from your "Remember List" or disable "Photos Activity" altogether to stop feedback tracking. Google Photos emphasizes:
"Your personal data in Photos is never used for ads" [20].
If these measures don’t work and your photos are misused, there are additional steps you can take.
What to Do If Your Photos Are Misused
If someone shares your AI-generated photos without your consent, act quickly. Document the misuse as evidence for potential legal action and contact the platform hosting the images to request their removal [18]. Platforms like Tinder allow users to exercise their "Right to Erasure" through account settings or by contacting support [15]. If your request is denied and you live in states like Texas, Oregon, Virginia, or Colorado, you have the right to appeal the decision [15].
For additional assistance, reach out to the Cyber Civil Rights Initiative (CCRI) Safety Center via their Image Abuse Helpline at 1-844-878-CCRI [18]. The Federal Trade Commission also advises:
"If you believe or know that someone shared an intimate image or video of you, visit the Cyber Civil Rights Initiative's (CCRI) Safety Center for help deciding what to do" [18].
You can also report the issue to the Federal Trade Commission at ReportFraud.ftc.gov and consider contacting local law enforcement to create an official record.
At Dating Photo AI, we prioritize your ability to control your data. We provide clear, easy-to-use options for managing your photos and personal information, helping you maintain privacy and security throughout your experience on our platform.
Conclusion
Understanding who owns your data is key to safeguarding your privacy and digital identity. While many platforms claim to assign ownership of AI-generated outputs to you, U.S. law specifies that content created solely by machines, without meaningful human input, cannot be copyrighted [1]. This legal gray area underscores the importance of choosing platforms wisely.
Opt for platforms with clear and transparent policies. Prioritize services that delete your images immediately after processing, avoid using your photos to train AI models, and offer straightforward data deletion options.
At Dating Photo AI, we take your data security and privacy seriously. Using advanced AI tools, we help you create stunning dating profile photos designed to boost your matches, all while adhering to strict data protection standards. We ensure clear ownership terms and provide robust data handling and deletion options, so you remain in full control of your personal information.
Before uploading your photos, always review a platform's privacy policies and terms. Look for details like whether they require "perpetual, irrevocable" licenses to your likeness, how long they retain your data, and whether they use your photos for AI training. Paid or business-grade tiers often come with stronger privacy protections, including "no training by default" policies [1].
Your face is one of a kind. By staying informed about data ownership and choosing platforms that respect your privacy, you can enhance your dating profile with confidence while keeping your personal information secure.
FAQs
How can I make sure my photos aren’t used to train AI without my permission?
To keep your photos from being used in AI training, start by checking the platform's privacy settings. Look for an option to opt out of AI training and enable it before uploading any images. If the platform doesn’t offer this option, you might decide against uploading your photos or reach out to the platform directly to request their removal. It’s also a good idea to carefully review the platform’s privacy policy to get a clear picture of how your data is managed.
How can I delete my data from an AI dating photo platform?
To remove your data from an AI-powered dating photo service, start by checking the platform’s privacy policy or terms of service. These documents often outline the steps for data deletion. Most services offer an option to delete your account directly through their app or website. Some may also let you submit a formal request for data removal. Look for sections like 'Data Deletion' or 'Account Closure' to find detailed instructions.
If the platform stores your uploaded images, see if they’re automatically deleted after processing. If not, you can usually remove them manually from your account. Alternatively, reach out to the platform’s support team for help. Once you’ve completed the process, consider clearing cookies or local storage from your browser to erase any leftover identifiers. It’s also wise to save confirmation emails or reference numbers related to your deletion request for future reference.
What does it mean if a platform has a 'perpetual, worldwide, royalty-free' license to use my photos?
When you agree to a platform's perpetual, worldwide, royalty-free license, you're essentially allowing them to use, alter, distribute, and even profit from your photos indefinitely - without any payment or further permission from you. This could mean your images might be used for things like training AI models, creating new works based on your photos, or other commercial activities.
The downside? You lose control over how your photos are used. There’s also the risk of privacy breaches or your likeness being used in ways you never intended. And here’s the kicker: these licenses are often permanent, so once you grant it, you can’t take it back. Always take the time to carefully read the platform’s terms to fully understand what you’re agreeing to when it comes to your personal data.
